In today’s rapidly industrializing world, sustainable wastewater management has become a pressing priority. One of the most critical technologies enabling efficient and accurate flow measurement in sewage treatment facilities is the electromagnetic flow meter. These devices have become indispensable tools in municipal and industrial wastewater systems, offering precise, reliable, and low-maintenance solutions for flow monitoring.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the application of electromagnetic flow meters in sewage treatment plants, uncover their advantages, discuss where and how they are used, and why they are the top choice for engineers and plant operators around the globe.
What Is an Electromagnetic Flow Meter?
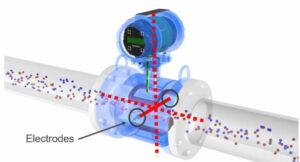
An electromagnetic flow meter, often referred to as a magmeter, is a type of flow measurement device that works based on Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction. This principle states that a voltage is induced when a conductive fluid flows through a magnetic field. That induced voltage is directly proportional to the flow velocity of the liquid.
Unlike traditional mechanical meters, electromagnetic flow meters have no moving parts, making them particularly well-suited for harsh and dirty environments like sewage treatment plants.
Why Electromagnetic Flow Meters Are Ideal for Sewage Applications
Electromagnetic flow meters are engineered specifically for conductive fluids, which makes them an excellent fit for wastewater, sludge, slurry, and other effluents typically found in sewage systems.
Here are several compelling reasons why electromagnetic flow meters excel in sewage applications:
-
Non-intrusive measurement: No moving parts or obstructions in the pipe.
-
High accuracy: Typically ±0.2% to ±0.5% of flow rate.
-
Excellent for dirty liquids: Capable of handling solids, debris, and high-viscosity substances.
-
Minimal maintenance: Low risk of clogging or mechanical failure.
-
Long-term stability: Reliable operation over years without frequent recalibration.
Key Areas of Application in Sewage Treatment Plants
Electromagnetic flow meters are used throughout the entire sewage treatment process, from the inlet of raw wastewater to the discharge of treated effluent. Let’s look at some specific applications.
1. Influent Monitoring
At the entry point of the sewage treatment plant, influent flow monitoring is essential for process control and capacity planning. Electromagnetic flow meters measure the volume and rate of incoming wastewater, helping to:
-
Detect flow surges
-
Monitor peak inflows during storms
-
Balance treatment load across units
2. Pumping Stations
In lift stations and transfer pumps, where wastewater is moved between different elevations or process stages, accurate flow measurement ensures pumps operate efficiently and avoid overloading. Magmeters withstand high turbulence and variable flow rates in these systems.
3. Grit Removal Systems
In grit chambers, flow rate needs to be maintained within optimal limits to allow heavy particles to settle. Electromagnetic flow meters help regulate flow velocity, supporting effective removal of grit without damaging downstream equipment.
4. Primary and Secondary Clarifiers
Magmeters are installed to measure flows between clarification tanks, ensuring the proper retention time and efficient removal of suspended solids. By maintaining correct flow rates, they help optimize sedimentation.
5. Sludge Handling and Return Activated Sludge (RAS)
Flow monitoring of thickened sludge and activated sludge returns is challenging due to the high solids content. Fortunately, electromagnetic flow meters perform exceptionally well in these conditions, offering accurate, clog-free measurement even with 10%+ solids content.
6. Chemical Dosing Control
Electromagnetic flow meters help control the precise dosing of chemicals such as coagulants, disinfectants, or pH stabilizers. Proper chemical dosing improves treatment efficiency and ensures compliance with discharge regulations.
7. Effluent Monitoring and Discharge Reporting
Before treated water is discharged into receiving bodies or reused, flow measurement is vital for regulatory compliance. Magmeters help ensure:
-
Compliance with flow permits
-
Accurate billing for industrial users
-
Reliable environmental reporting
8. Biological Reactor and Aeration Control
Flow control in aeration basins is critical to maintain optimal microbial activity. Too much or too little flow can upset the treatment process. Electromagnetic flow meters provide stable and responsive measurements to support process automation.
9. Energy Optimization
By closely monitoring flow at various points, treatment plants can optimize pump operation, reduce energy use, and improve overall process efficiency. Flow data enables predictive maintenance and system diagnostics.
10. SCADA and Remote Monitoring Integration
Modern electromagnetic flow meters offer digital communication protocols like Modbus, HART, and Profibus, making them easy to integrate into SCADA systems. This enables remote monitoring, data logging, and advanced diagnostics for predictive maintenance.
Technical Features That Enhance Magmeter Performance
To perform optimally in sewage treatment, electromagnetic flow meters often include the following features:
-
Ceramic or PTFE liners: Resist corrosion and abrasion.
-
Stainless steel or Hastelloy electrodes: Withstand aggressive media.
-
IP68 waterproofing: Suitable for submerged installations.
-
Bidirectional flow capability: Measure flow in both directions.
-
Empty pipe detection: Prevent false readings in partially filled pipes.
Case Study: Boosting Accuracy and Reducing Downtime in a Municipal Plant
A wastewater treatment plant in Germany replaced outdated mechanical meters with electromagnetic flow meters in its sludge return lines. The old meters frequently clogged and required weekly maintenance. After switching to magmeters:
-
Maintenance dropped by 80%
-
Flow accuracy improved by 25%
-
Annual operating costs were reduced by 30%
This example highlights how upgrading to electromagnetic flow meters results in greater reliability, reduced costs, and improved environmental performance.
How to Choose the Right Electromagnetic Flow Meter
When selecting a magmeter for sewage applications, consider the following:
-
Pipe size – Make sure the flow meter matches your pipeline diameter.
-
Flow range – Choose a model with appropriate turndown ratio.
-
Chemical compatibility – Verify the liner and electrode materials suit your wastewater composition.
-
Installation environment – Consider whether it’s exposed, submerged, or in a hazardous area.
-
Communication protocols – Ensure compatibility with your control system.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Although magmeters are low-maintenance, some common challenges include:
-
Build-up on electrodes: Can be avoided with self-cleaning designs or electrode cleaning routines.
-
Incorrect grounding: Ensure proper grounding to avoid signal noise.
-
Empty pipe alarms: Use installation best practices to maintain full pipe conditions.
Proactive commissioning, calibration, and training of personnel can help maximize meter lifespan and maintain high data integrity.
The Future of Flow Measurement in Wastewater Treatment
As the world moves toward smarter infrastructure and sustainability goals, electromagnetic flow meters will play a growing role in:
-
IoT-enabled monitoring
-
Automated process control
-
Real-time leakage detection
-
Performance-based plant optimization
The integration of AI-driven analytics with flow data will allow utilities to make better operational decisions and respond faster to anomalies.
Conclusion
The application of electromagnetic flow meters in sewage treatment plants has revolutionized how wastewater flow is measured, monitored, and controlled. Their accuracy, durability, and compatibility with challenging fluid types make them the go-to solution for municipal and industrial treatment systems alike.
From influent tracking and sludge monitoring to chemical dosing and discharge reporting, electromagnetic flow meters contribute at every stage of the process. By choosing the right meter and integrating it effectively into your plant’s control system, you can optimize performance, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with environmental standards.
In an era where efficiency and sustainability are paramount, electromagnetic flow meters are more than just tools—they’re essential partners in building a cleaner, more resilient future.