In the world of engineering, fluid dynamics plays a critical role in various industrial and scientific applications. One fundamental concept in fluid dynamics is flow rate, a key parameter that determines how much fluid moves through a system in a given time. Whether you’re working with water treatment systems, oil pipelines, or chemical reactors, understanding flow rate is essential for maintaining efficiency and ensuring the safety and effectiveness of operations.
In this article, we will explore what flow rate is, the different types of flow rates, how it’s measured, and its importance in various industries. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of flow rate’s definition, its measurement techniques, and its real-world applications.
What is Flow Rate?
Simply put, flow rate refers to the volume of fluid that passes through a given point in a system per unit of time. It is a measure of how quickly or slowly fluid moves through pipes, tubes, or open channels. Flow rate can be expressed in several units depending on the type of fluid and the specific measurement system in use. Common units for flow rate include:
-
Liters per minute (L/min)
-
Gallons per minute (GPM)
-
Cubic meters per second (m³/s)
-
Cubic feet per minute (CFM)
In essence, flow rate helps engineers and operators understand how much fluid is moving, which is crucial for ensuring the proper function of the system.
Why is Flow Rate Important?
Flow rate is a crucial parameter in various industries for several reasons. For example:
-
Efficiency and Safety: In industrial applications, maintaining the correct flow rate ensures that systems operate at their optimal efficiency. If the flow rate is too high or too low, it could cause equipment failure, inefficiency, or even safety hazards.
-
Process Control: In processes such as chemical production or wastewater treatment, precise control of the flow rate is necessary to maintain product quality and meet regulatory standards.
-
System Design: Engineers use flow rate data to design pipes, pumps, and valves. For example, the size and pressure rating of a pump depend on the flow rate requirements of the system.
In short, flow rate affects the functionality and safety of numerous systems, making it a key factor in engineering design and maintenance.
Types of Flow Rate
Flow rate isn’t a one-size-fits-all measure. There are different types of flow rate depending on the conditions and the type of fluid involved. The three primary categories of flow rate are:
1. Volumetric Flow Rate
The volumetric flow rate is the most commonly used type of flow rate. It measures the volume of fluid that passes through a given area in a set amount of time. This is typically expressed as:
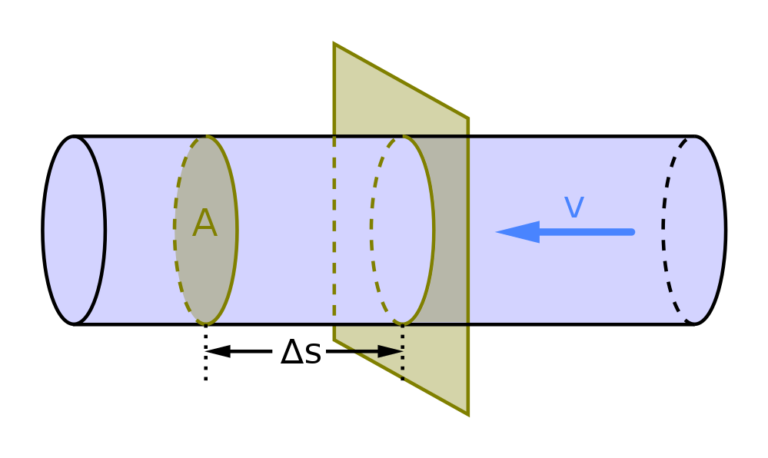
-
Q = V/t, where:
-
Q is the volumetric flow rate,
-
V is the volume of fluid,
-
t is the time.
-
This flow rate is usually measured in units like liters per second (L/s) or gallons per minute (GPM).
2. Mass Flow Rate
The mass flow rate measures the mass of fluid passing through a given point per unit of time. This type of flow rate is used when the density of the fluid is important, such as in systems dealing with oil, gas, or chemical substances. The mass flow rate is calculated as:
-
m = ρ * A * V, where:
-
m is the mass flow rate,
-
ρ is the density of the fluid,
-
A is the cross-sectional area of the pipe,
-
V is the velocity of the fluid.
-
Mass flow rate is commonly measured in kilograms per second (kg/s) or pounds per hour (lb/h).
3. Volumetric vs. Mass Flow Rate: Key Differences
While both volumetric and mass flow rate measure fluid movement, they differ in the type of measurement they provide. Volumetric flow rate is ideal for systems where the volume of fluid is of concern, such as water distribution systems. Mass flow rate, on the other hand, is critical when the weight of the fluid or the material’s density must be accounted for, like in the case of gases or oils.
How is Flow Rate Measured?
Measuring flow rate is a vital task that requires the right tools and methods. Several techniques can be used, depending on the fluid type, the system configuration, and the required accuracy. Here are the most common methods for measuring flow rate:
1. Positive Displacement Flow Meters
Positive displacement flow meters are commonly used for low to moderate flow rates. These devices work by capturing a fixed volume of fluid in each cycle and counting the number of cycles to determine the flow rate. They are highly accurate and commonly used in oil and gas measurement.
2. Turbine Flow Meters
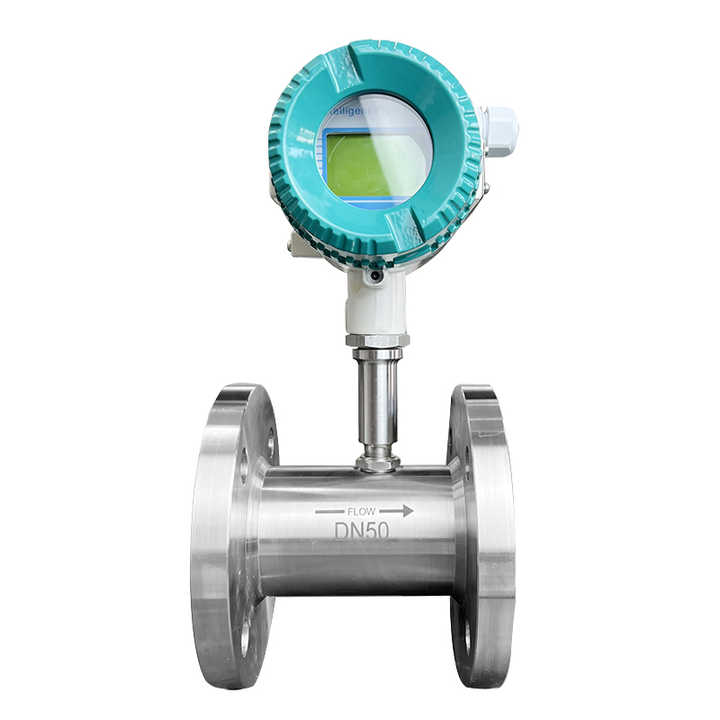

Turbine flow meters work by using a rotating turbine to measure the velocity of the fluid. As the fluid passes through the meter, it causes the turbine to rotate, and the flow rate is calculated based on the rotational speed of the turbine. These are ideal for high-velocity flows.
3. Electromagnetic Flow Meters
Electromagnetic flow meters are commonly used for conductive fluids, such as water and sewage. They work on the principle of Faraday’s Law of Induction, where the fluid flowing through a magnetic field induces a voltage, which is proportional to the velocity of the flow. These meters offer high accuracy and are ideal for wastewater treatment.
4. Ultrasonic Flow Meters
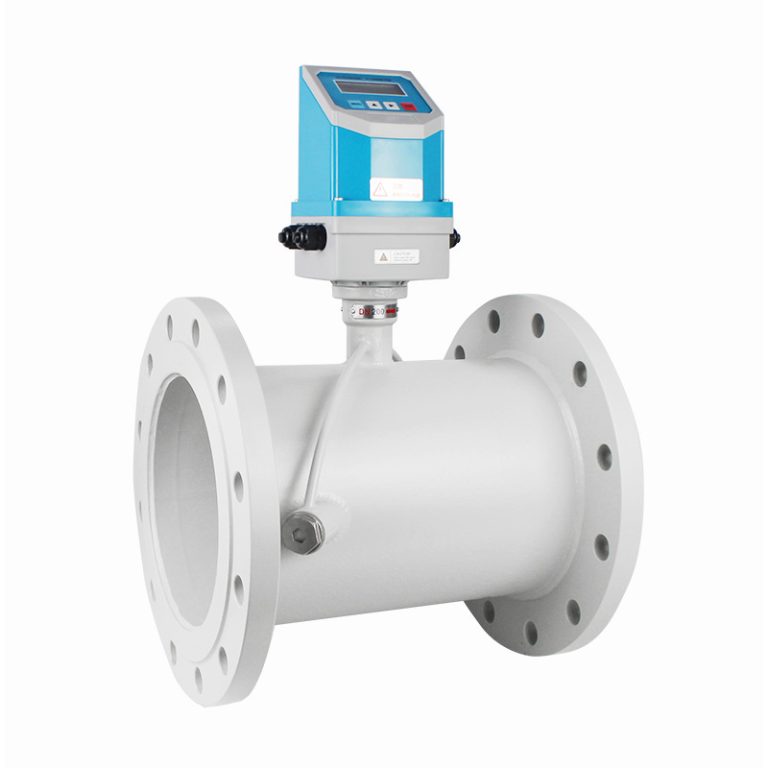

Ultrasonic flow meters use sound waves to measure the flow rate. There are two types of ultrasonic flow meters: transit-time and Doppler. Transit-time meters measure the time it takes for sound waves to travel with and against the flow, while Doppler meters measure the frequency shift of sound waves reflected off particles in the fluid. They are particularly useful for non-invasive flow measurement.
5. Vortex Flow Meters
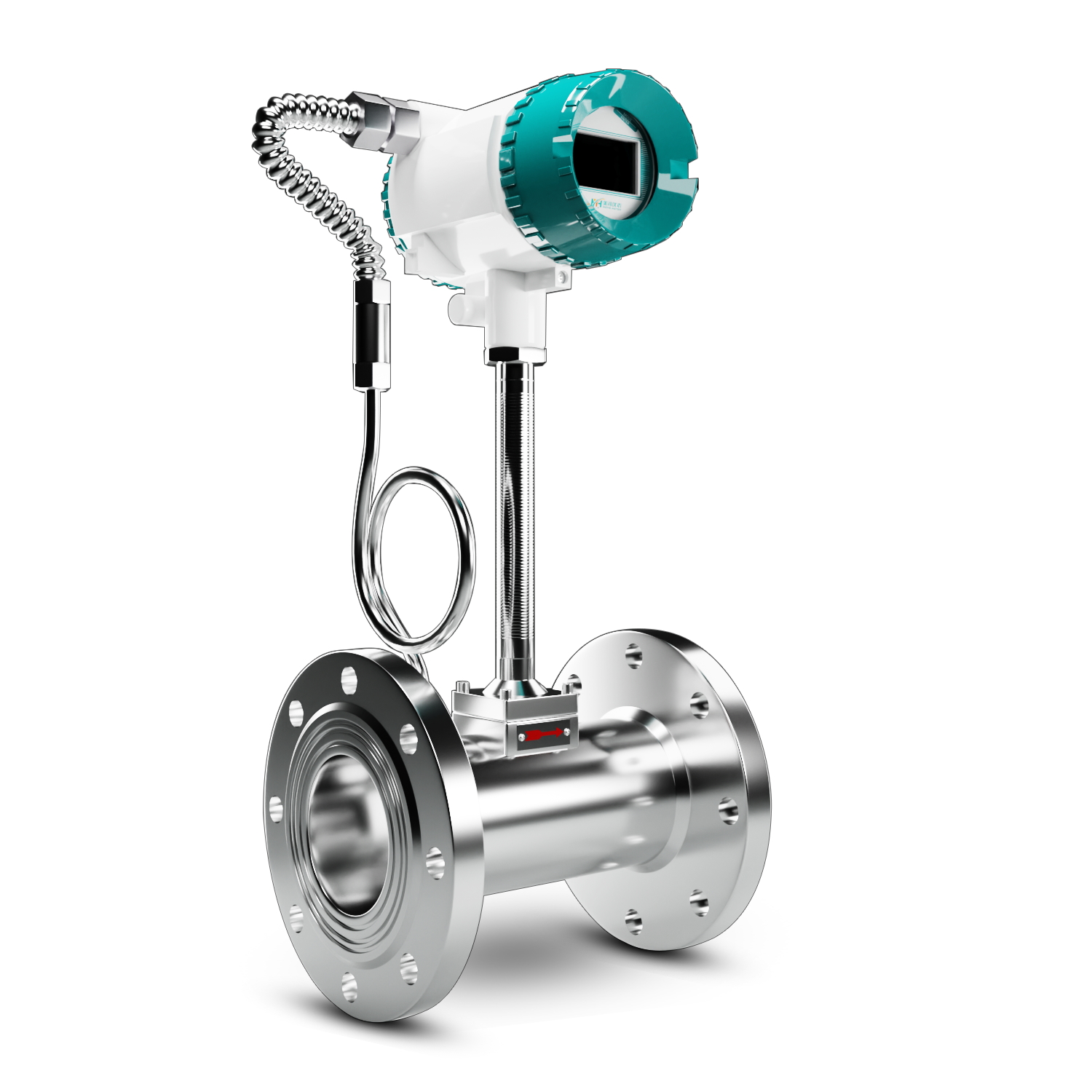

Vortex flow meters work by measuring the frequency of vortices formed as fluid passes a bluff body. These meters are ideal for measuring the flow of gases, steam, and liquids in industrial applications.
Flow Rate in Different Industries
Flow rate measurement is essential in many industries, each with its unique requirements for accuracy and precision. Here’s a look at a few key industries:
1. Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas industry, accurate flow rate measurement is essential for monitoring the flow of oil and natural gas from extraction points to processing plants and refineries. Mass flow meters are typically used in these applications because they can account for changes in fluid density and provide precise measurements.
2. Water Treatment
In water treatment plants, accurate flow measurement is essential for controlling the intake and treatment of water. Volumetric flow meters are often used to measure the water flow in pipes and channels to ensure the plant operates efficiently.
3. Chemical Processing
In the chemical industry, flow rate measurements are crucial for mixing, blending, and controlling the flow of various chemicals. Both volumetric and mass flow meters are used depending on the application, with an emphasis on mass flow meters when dealing with dense or viscous fluids.
4. HVAC Systems
In HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, measuring the flow rate of air and water is important for maintaining optimal performance and energy efficiency. Airflow meters and water flow meters are commonly used to monitor system performance and adjust as needed.
The Impact of Flow Rate on System Efficiency
Flow rate plays a significant role in the efficiency of a system. Whether it’s a pump, turbine, or pipe network, flow rate directly affects the pressure, velocity, and energy consumption of the system. Here are some ways flow rate impacts system efficiency:
-
Energy Consumption: A higher flow rate requires more energy to pump the fluid, while a lower flow rate might not meet the system’s operational requirements.
-
Wear and Tear: Excessive flow rates can lead to erosion or corrosion in pipes and equipment, leading to costly repairs and downtime.
-
Optimal Performance: Ensuring the correct flow rate helps maintain the balance between efficiency, energy consumption, and system longevity.
Conclusion
In summary, flow rate is an essential concept in fluid dynamics, impacting industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, chemical processing, and HVAC systems. Whether you are measuring volumetric flow, mass flow, or using different types of flow meters, understanding and controlling flow rate is crucial for system optimization, safety, and efficiency. By selecting the appropriate flow measurement method, industries can ensure precise control and efficient operation.
We are a manufacturer of automatic flow meters with many years of experience in the industry. We have strong independent research and development capabilities and are a leader in the flow meter industry. Our main products include electromagnetic flow meters, vortex flow meters, turbine flow meters, ultrasonic flow meters, Coriolis flow meters, various solenoid valves, level meters, control units and valves, etc. Welcome to purchase –Best Instrument





