In a world where precision and reliability are more critical than ever, electromagnetic flowmeters have emerged as a cornerstone technology for accurate fluid flow measurement. Whether you’re operating in water treatment, chemical manufacturing, or food and beverage processing, chances are you’ve encountered¡ªor should consider¡ªthis game-changing flow measurement tool.
In this guide, we’ll take a deep dive into how electromagnetic flowmeters work, their core benefits, typical applications, and key buying considerations, all in a way that’s clear, engaging, and packed with valuable insights.
What Is an Electromagnetic Flowmeter?

An electromagnetic flowmeter, often called a mag meter, is a type of flow measurement device that uses Faraday¡¯s Law of Electromagnetic Induction to determine the flow rate of liquid passing through a pipe.
At its core, this device measures volumetric flow rate¡ªnot mass or velocity¡ªmaking it ideal for measuring conductive liquids like water, slurries, and certain chemicals. What sets it apart is that it has no moving parts, which means low maintenance and exceptional durability.
How Do Electromagnetic Flowmeters Work?
Understanding the principle is easier than it sounds.
https://youtu.be/EbMmTJNJOZE?si=VY9LGdLrYQfXIShMAccording to Faraday’s Law, when a conductive liquid flows through a magnetic field, it generates a voltage. The faster the liquid moves, the greater the voltage. Electrodes placed in the walls of the flow tube pick up this voltage, and the meter’s electronics convert it into a flow rate.
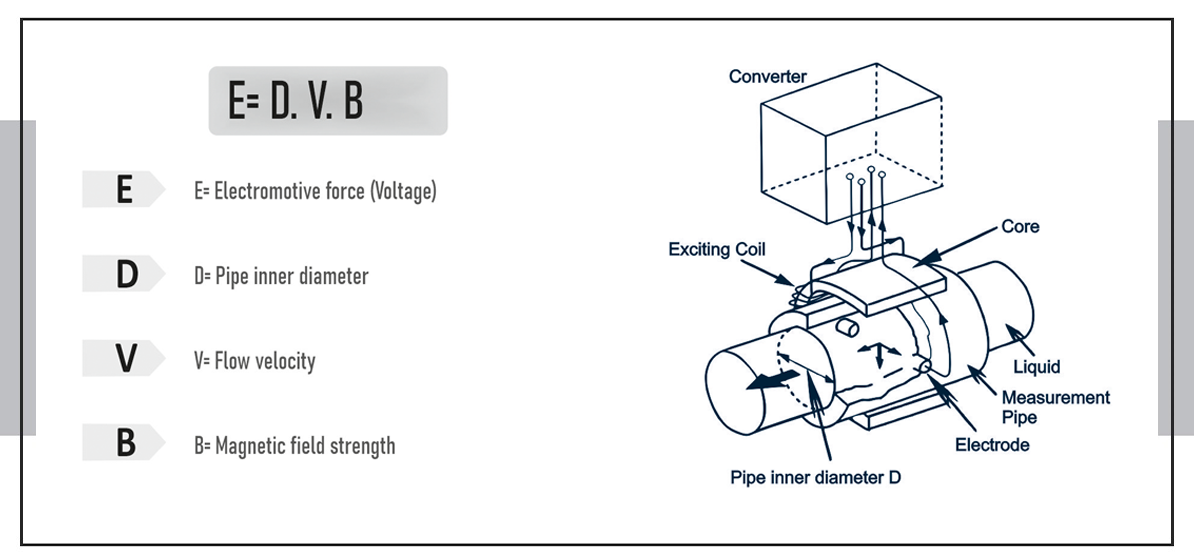
Simple formula:
E = k ¡Á B ¡Á D ¡Á V
Where:
E is the induced voltage
k is a constant
B is the magnetic field strength
D is the diameter of the pipe
V is the velocity of the fluid
In short, the flowmeter translates physics into precise numbers, giving you a clear understanding of how much fluid is moving and at what rate.
Key Components of an Electromagnetic Flowmeter
To truly appreciate how smart this technology is, it helps to know what it’s made of:
Flow Tube ¨C The pipe section through which the fluid flows. Often lined with non-conductive material.
Magnetic Coils ¨C Generate a magnetic field across the flow tube.
Electrodes ¨C Detect the voltage generated by the flowing conductive liquid.
Transmitter ¨C Converts the voltage signal into a readable flow value.
Each part is optimized for accuracy, stability, and long-term use, even in harsh industrial environments.
Advantages of Using Electromagnetic Flowmeters
Electromagnetic flowmeters are packed with benefits that make them a top choice in many industries:
1. High Accuracy
Most mag meters boast an accuracy level of ¡À0.2% to ¡À0.5%, which is more than sufficient for most industrial applications.
2. No Moving Parts
Unlike turbine or paddlewheel meters, electromagnetic meters don¡¯t wear out quickly because there are no moving components. This translates into lower maintenance costs and longer lifespan.
3. Minimal Pressure Loss
The design ensures unrestricted flow, meaning pressure drop is practically non-existent.
4. Versatility
They work with a wide range of fluids¡ªfrom clean water to viscous slurries¡ªas long as the fluid is electrically conductive.
5. Smart Features
Modern mag meters come with digital transmitters, remote monitoring, diagnostics, and data logging¡ªmaking them ideal for IoT and automation applications.
Limitations You Should Know
As powerful as they are, electromagnetic flowmeters have their limitations:
They only work with conductive fluids. Non-conductive fluids like oils and gases are a no-go.
Initial installation costs can be higher than simpler flow meters.
Proper grounding and correct installation are crucial to avoid signal noise or erratic readings.
But when used correctly, these limitations are minor compared to the benefits.
Common Industries Using Electromagnetic Flowmeters
Water and Wastewater Management
Municipal water utilities rely heavily on mag meters for billing, leak detection, and treatment processes. Their reliability and low maintenance make them ideal for long-term infrastructure.
Chemical Processing
In this industry, measuring corrosive and viscous fluids with high accuracy is essential. Mag meters handle this with ease, especially when paired with chemical-resistant linings.
Food and Beverage
Sanitary mag meters are used in the production of milk, beer, and juices. They ensure hygienic processing and precise recipe control.
Pulp and Paper
Slurries and fibrous materials require robust and accurate flow measurement¡ªperfect territory for electromagnetic flowmeters.
Mining and Metals
Harsh environments and abrasive fluids are no match for heavy-duty mag meters designed with wear-resistant liners.
Installation Best Practices
Getting the most out of your electromagnetic flowmeter starts with correct installation. Here are some key tips:
Ensure proper grounding to eliminate signal noise.
Avoid installing near electrical equipment that could cause electromagnetic interference.
Use straight pipe sections before and after the meter (typically 5¨C10 diameters upstream and 3¨C5 downstream) to ensure accurate readings.
Mount the flowmeter horizontally with electrodes in a horizontal plane to avoid air bubble interference.
Following these practices ensures optimum performance and data accuracy.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Even though they¡¯re low-maintenance, regular checks can extend the lifespan of your electromagnetic flowmeter:
Inspect electrodes periodically for fouling or buildup.
Calibrate annually to maintain measurement accuracy.
Update firmware if your meter includes a digital transmitter.
Keep logs of flow readings to detect abnormalities early.
A small effort in maintenance can translate into years of flawless operation.
How to Choose the Right Electromagnetic Flowmeter
Here are the most important factors to consider:
Fluid Conductivity ¨C Ensure the fluid is conductive enough, typically more than 5 ¦ÌS/cm.
Pipe Size ¨C Choose a meter that matches your system¡¯s pipe diameter.
Liner Material ¨C For corrosive fluids, go with chemically resistant liners like PTFE or PFA.
Output Signals ¨C Select analog or digital outputs compatible with your SCADA or PLC system.
Certifications ¨C Look for industry-specific certifications like 3A for food, ATEX for hazardous environments, or ISO compliance.
Buying the right meter is not just a cost¡ªit¡¯s a strategic investment in operational efficiency.
The Future of Flow Measurement: Smart Mag Meters
Technology continues to evolve, and mag meters are no exception. The newest models are equipped with:
Bluetooth connectivity
Cloud-based monitoring
Real-time alerts
Advanced diagnostics
These features make them a perfect fit for smart factories, automated facilities, and remote operations where real-time data is crucial.
Expect mag meters to play a leading role in Industry 4.0 and sustainability initiatives, thanks to their energy-efficient design and remote capabilities.
Conclusion: Why Electromagnetic Flowmeters Are a Smart Choice
In today¡¯s world, where every drop counts and precision is power, electromagnetic flowmeters are clearly one of the best tools available for accurate and reliable fluid measurement. With their cutting-edge technology, minimal maintenance, and versatile applications, these meters are a smart, future-ready solution for a wide range of industries.
If you need real-time insights, dependable performance, and long-term value, investing in a mag meter isn¡¯t just smart¡ªit¡¯s essential.
We are a manufacturer of automatic flow meters with many years of experience in the industry. We have strong independent research and development capabilities and are a leader in the flow meter industry. Our main products include electromagnetic flow meters, vortex flow meters, turbine flow meters, ultrasonic flow meters, Coriolis flow meters, various solenoid valves, level meters, control units and valves, etc. Welcome to purchase –Best Instrument
